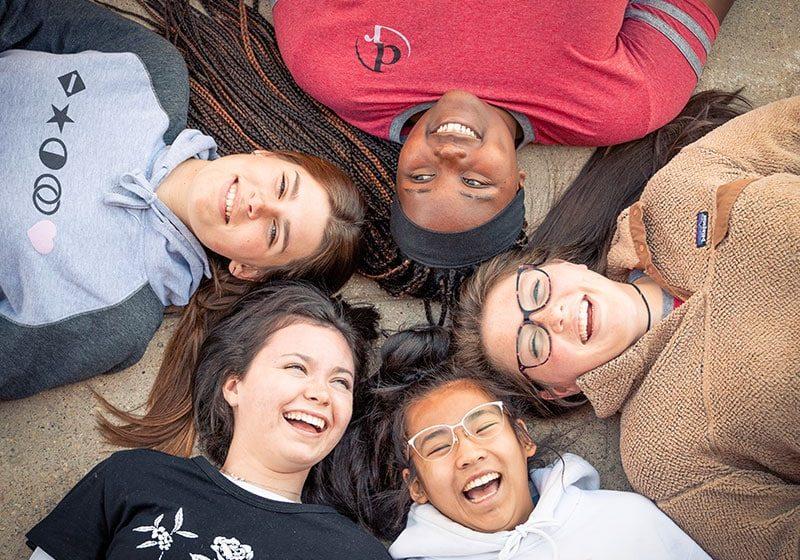
Adolescence is a time of immense physical, emotional, and psychological growth, but for some young people, the experience of trauma can disrupt this important developmental stage. Trauma, whether caused by abuse, neglect, loss, or witnessing violence, can have lasting effects on an adolescent’s mental health and behavior. These experiences can lead to a range of issues such as depression, anxiety, substance abuse, self-harm, and difficulties with relationships and school performance.
In these cases, adolescent trauma residential treatment can provide an effective solution. Residential treatment centers (RTCs) offer a safe, structured environment where adolescents can receive intensive care and therapy tailored to their unique needs. This type of treatment allows young individuals to work through their trauma in a supportive, therapeutic setting, helping them heal and develop healthier coping mechanisms for the future.
This article explores what adolescent trauma residential treatment entails, how it works, and why it is such an essential resource for teens struggling with the effects of trauma.
1. What is Adolescent Trauma Residential Treatment?
Adolescent trauma residential treatment refers to a specialized type of therapy offered in residential treatment centers for teens who have experienced significant trauma. It combines therapeutic interventions with 24/7 supervision and support to create a safe and healing environment for adolescents.
These facilities provide a holistic, trauma-informed approach to healing, recognizing the unique challenges that trauma survivors face and offering treatment that addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological effects of trauma. The goal is to help teens process their trauma, develop healthier coping strategies, and build resilience to prevent the lasting impact of trauma on their future.
2. Why Trauma-Informed Treatment is Crucial for Adolescents
Adolescents are particularly vulnerable to the effects of trauma due to the rapid changes they are experiencing both physically and emotionally. During this developmental stage, young people are still learning how to regulate their emotions, form relationships, and understand their identity. Experiencing trauma during these formative years can disrupt this development, leading to emotional and behavioral difficulties that can persist into adulthood.
Trauma can affect adolescents in many different ways, including:
-
Emotional distress: Feelings of sadness, anger, guilt, shame, or hopelessness.
-
Behavioral issues: Engaging in risky or destructive behaviors such as substance abuse, self-harm, or aggression.
-
Difficulty in relationships: Challenges in forming and maintaining healthy relationships with family, friends, or peers.
-
Academic struggles: Poor performance in school or disengagement due to difficulty concentrating or a lack of motivation.
-
Mental health issues: Conditions such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and dissociation can develop as a result of trauma.
Because adolescents are still learning how to manage and express their emotions, trauma can be especially confusing and overwhelming. Traditional therapeutic approaches may not always be effective for young people, which is why trauma-informed residential treatment is so important. These programs recognize the impact of trauma and work specifically to address it in a way that acknowledges the teen’s emotional and developmental needs.
3. Key Components of Adolescent Trauma Residential Treatment
Residential treatment centers that specialize in trauma-informed care provide a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach to healing. Some of the key components of these programs include:
3.1. Trauma-Focused Therapy
The cornerstone of any adolescent trauma residential treatment program is therapy. Several therapeutic modalities may be used to help teens process their trauma and learn how to cope with their emotions. Common therapies used in these settings include:
-
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT): TF-CBT is specifically designed to help children and adolescents process trauma. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns related to the traumatic experience and helping teens build healthier coping mechanisms.
-
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): DBT helps teens regulate their emotions, improve relationships, and develop mindfulness skills. It is particularly helpful for teens who struggle with intense emotions and behaviors, such as self-harm or suicidal ideation.
-
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing): EMDR is a type of therapy designed to help individuals process traumatic memories by using bilateral stimulation (e.g., eye movements) to reduce the distress associated with traumatic memories.
-
Group Therapy: Group therapy provides a space for teens to connect with others who have experienced similar trauma, offering a sense of community and support. Group therapy can help adolescents share their feelings, learn from others, and feel less isolated.
3.2. 24/7 Supervision and Support
Adolescents in residential treatment facilities are provided with constant supervision to ensure their safety and well-being. This structure is critical for teens who may have trouble regulating their emotions or engaging in dangerous behaviors due to trauma. Around-the-clock support from trained staff provides both physical and emotional security as teens work through their healing journey.
3.3. Holistic Approach to Healing
Trauma affects every aspect of a teen’s life, so effective treatment takes a holistic approach to healing. In addition to therapy, teens in residential treatment centers often participate in a variety of activities designed to promote overall well-being:
-
Physical activities: Exercise, yoga, or outdoor activities can help teens release pent-up emotions, improve their physical health, and reduce stress.
-
Creative therapies: Art, music, and drama therapy allow teens to express their emotions in non-verbal ways, which can be especially beneficial for those who find it difficult to talk about their trauma.
-
Life skills development: Teens in residential treatment centers often engage in activities designed to help them develop essential life skills, such as communication, problem-solving, and decision-making. These skills will help them navigate challenges long after they leave the program.
3.4. Family Involvement
Trauma can have a significant impact on family dynamics, and it is often important for the family to be involved in the healing process. Many adolescent trauma residential treatment programs include family therapy sessions to help rebuild trust, improve communication, and address any issues that may have contributed to the teen’s trauma. Family support is often critical for long-term success in recovery.
3.5. Education and Academic Support
For teens who are still in school, education is an essential part of their treatment plan. Residential treatment centers often provide on-site educational programs to ensure that teens continue their academic progress while in treatment. These programs are tailored to each teen’s needs, offering individualized support to help them stay on track with their studies while also focusing on their emotional well-being.
4. The Benefits of Adolescent Trauma Residential Treatment
Adolescent trauma residential treatment offers numerous benefits for teens struggling with the effects of trauma. Some of the key benefits include:
-
Safe and structured environment: Residential treatment centers provide a stable, secure environment where teens can focus on healing without the distractions or pressures of daily life.
-
24/7 access to care: With constant supervision and support, teens in residential treatment have access to immediate help whenever they need it, especially during times of emotional distress.
-
Comprehensive treatment: These programs address not just the symptoms of trauma but also the underlying causes, helping teens to heal holistically and build resilience for the future.
-
Long-term healing: By addressing trauma early, adolescents can develop healthy coping mechanisms and emotional regulation skills that will serve them for the rest of their lives.
-
Family involvement: Family therapy and support ensure that the healing process extends beyond the teen and into the home, providing lasting positive change.
5. Conclusion
Adolescent trauma residential treatment plays a vital role in helping young people who have experienced trauma heal and move forward in a healthy, productive way. By offering a safe, supportive environment, trauma-focused therapy, and comprehensive care, residential treatment centers provide the tools needed for teens to address their trauma, improve their mental health, and create a foundation for a brighter future.
If your teen has experienced trauma and is struggling with emotional or behavioral issues, seeking help from a trauma-informed residential treatment program can be the first step toward healing and recovery. With the right support, your adolescent can learn to overcome their trauma, rebuild their sense of self-worth, and lead a more fulfilling life.