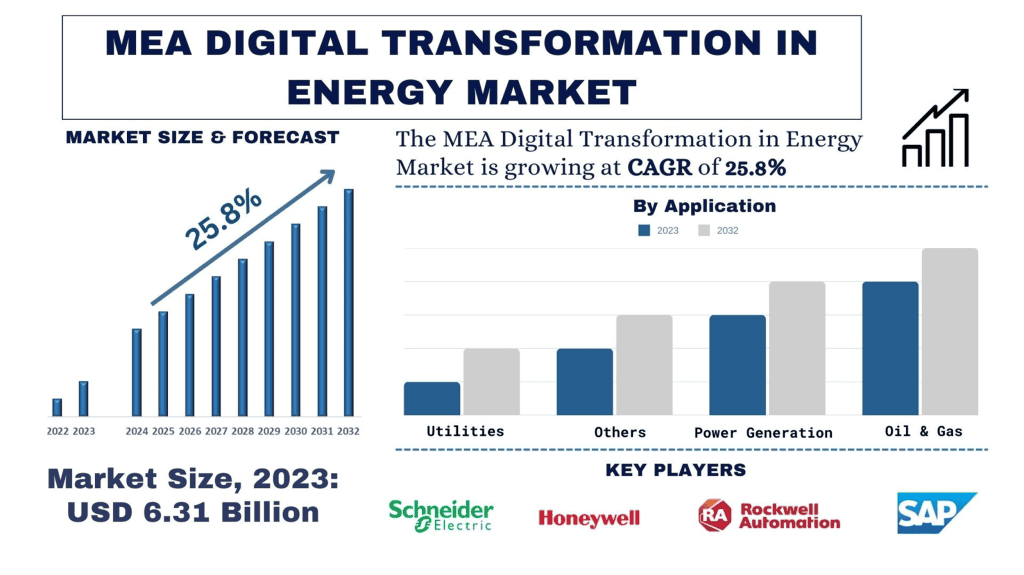
According to the UnivDatos, increasing investment in digital grid technologies in the region will drive the scenario of digital transformation in energy and as per their “MEA Digital Transformation in Energy Market” report, the Market was valued at USD ~6.31 billion in 2022, growing at a CAGR of 25.8% during the forecast period from 2024 - 2032 to reach USD billion by 2032.
In the dynamic landscape of the MEA region, the energy sector is experiencing a rapid digital transformation that is reshaping the way energy is produced, distributed, and consumed. To delve into the latest trends shaping this transformation, it becomes evident that technology is not just a tool but a catalyst for innovation, efficiency, and sustainability.
Renewable Energy Revolution:
One of the most prominent trends in the MEA energy market is the rapid expansion of renewable energy sources. Countries like the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia are investing heavily in solar and wind energy projects, aiming to diversify their energy mix and reduce dependency on fossil fuels. The UAE's Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park and Saudi Arabia's ambitious Vision 2030 plan are prime examples of the region's commitment to renewable energy. This trend not only aligns with global efforts to combat climate change but also presents significant economic opportunities for countries in the region.
Smart Grids and IoT Integration:
Another key trend driving the digital transformation of the MEA energy market is the adoption of smart grid technologies. Smart grids leverage advanced sensors, analytics, and communication technologies to optimize energy distribution, improve grid reliability, and enable efficient integration of renewable energy sources. Countries like Kuwait and South Africa are deploying smart grid solutions to modernize their aging infrastructure and enhance energy efficiency. By enabling real-time monitoring and control of energy networks, smart grids are empowering utilities to better manage demand, reduce losses, and mitigate disruptions.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures) - https://univdatos.com/reports/mea-digital-transformation-in-energy-market?popup=report-enquiry
Internet of Things (IoT) in Energy:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the energy sector by enabling the connectivity of devices and systems, thereby facilitating data-driven decision-making and automation. In the MEA region, IoT technologies are being deployed across the entire energy value chain, from oil and gas production to electricity distribution. For example, in Algeria, IoT sensors are being used to monitor pipeline networks and optimize maintenance schedules, leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Similarly, in South Africa, IoT-enabled smart meters are helping utilities track energy consumption patterns and implement demand-side management strategies.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are playing a crucial role in unlocking insights from the vast amounts of data generated by energy infrastructure. By leveraging AI algorithms and machine learning techniques, energy companies can optimize asset performance, predict equipment failures, and optimize energy production and consumption patterns. In countries like Egypt and Nigeria, AI-powered energy management systems are being deployed to optimize grid operations and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, AI-driven predictive maintenance solutions are helping energy companies reduce downtime, increase reliability, and extend the lifespan of critical assets.
Blockchain Technology in Energy Trading:
Blockchain technology is emerging as a disruptive force in the energy market, enabling secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. In the MEA region, blockchain-based energy trading platforms are being piloted to facilitate peer-to-peer energy transactions, allowing consumers to buy and sell excess energy directly to each other. This trend is particularly relevant in countries with high levels of renewable energy generation, such as Morocco and Kenya, where decentralized energy trading can help optimize the use of renewable resources and increase energy access in remote areas.
Cybersecurity Concerns:
Despite the numerous benefits of digital transformation in the energy sector, cybersecurity remains a significant concern. With the increasing connectivity of energy infrastructure and the proliferation of IoT devices, energy companies are facing a growing number of cyber threats. In response, governments and energy companies in the MEA region are ramping up their cybersecurity efforts, investing in advanced threat detection and response capabilities, and implementing robust security protocols to safeguard critical energy infrastructure from cyber attacks.
Conclusion
As the MEA region continues its journey toward a digitalized energy future, the trends outlined above underscore the transformative potential of technology in driving innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. From renewable energy expansion to smart grid deployment, from IoT adoption to AI-driven analytics, and blockchain-enabled energy trading to cybersecurity measures, the MEA energy market is witnessing a wave of innovation that promises to reshape the future of energy. By embracing these trends and leveraging digital technologies, countries in the MEA region can unlock new opportunities, drive economic growth, and build a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem for generations to come.
Contact Us:
Email - contact@univdatos.com
Website - www.univdatos.com