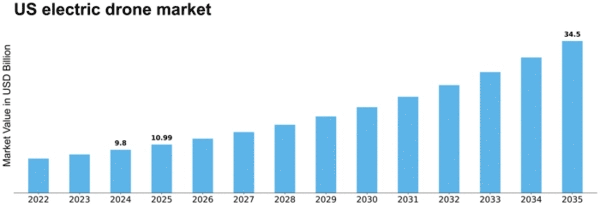
The narrative of electric drones in the U.S. is increasingly one of transformation: from hobbyist gadgets and early-adopter toys to mission-critical tools being deployed at scale by businesses, governments, and communities. The recent MRFR report paints a picture of a diversified, growing US electric drone market that encompasses multiple drone types (multirotor, fixed-wing, hybrid), broad application domains (from agriculture and mapping to surveillance, delivery, and infrastructure inspection), and multiple end-user categories including commercial enterprises, public agencies, military, and consumers.
Behind this shift lies rapid technological progress. Advances in battery and electric propulsion systems, smarter navigation and sensor integration, and lightweight materials are making electric drones far more capable than before — with longer flight durations, larger payloads, improved reliability, and expanded operational scopes. This evolution mirrors broader trends in the global electric drone market, which is projected to grow from USD 39.94 billion in 2024 to over USD 141.13 billion by 2035. Because the U.S. is a core region in this growth story, we can expect domestic drone adoption to scale significantly.
In agriculture, these drones are enabling precision farming — equipping farmers to monitor crops, assess soil health, and apply inputs more efficiently. In logistics and delivery, the pressure of online shopping and consumer demand for speed is encouraging businesses to invest in drone-based last-mile solutions. Electric drones — quieter, more environmentally friendly, and more nimble than traditional vehicles — are emerging as an attractive alternative. For public agencies and infrastructure operators, drones offer cost-effective ways to survey land, inspect assets, monitor environmental conditions, or respond to emergencies — often more quickly and safely than traditional methods.
The versatility of drone configurations also plays a major role in adoption. Multirotor drones, favored for their maneuverability and stability, dominate many commercial and consumer applications. Fixed-wing and hybrid models, however, bring advantages where endurance, range, or heavier payloads matter — supporting uses like surveying large areas, mapping, and cargo delivery. Payload capacity categories — ranging from under 2 kg to over 10 kg — allow for a wide spectrum of use cases: from lightweight photography drones to heavier-duty cargo or agricultural drones.
Looking forward, regulatory developments and evolving aviation policy will significantly shape the market. As rules around drone flights, BVLOS operations, and commercial drone usage become clearer and more accommodating, more organizations are likely to invest in drone technology. Combined with ongoing technological enhancements, this could accelerate the adoption of electric drones across sectors in the United States.
Ultimately, the US electric drone market is moving from early-stage hype to real, scalable impact. With solid growth forecasts, diverse applications, flexible drone types, and supportive regulation, electric drones are increasingly becoming indispensable tools — enabling smarter agriculture, faster delivery, efficient infrastructure monitoring, and more responsive emergency services. Stakeholders across industries should be watching closely: the sky is no longer the limit, it might well be the next big frontier.
More Report:
france aviation mro logistics market
germany aviation mro logistics market
japan aviation mro logistics market